Breast Reduction Surgery: What to Expect, Benefits, and Risks
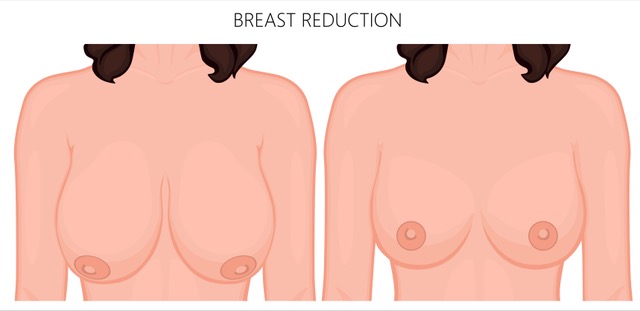
Breast reduction surgery, also known as reduction mammaplasty, is a procedure designed to remove excess breast tissue and reshape the breasts for improved comfort and aesthetics. This surgery is commonly sought by individuals experiencing physical discomfort due to large breasts, including back pain, neck pain, and skin irritation.
Addressing Breast Asymmetry in Surgery
If breast asymmetry was present before surgery, one of the goals of the procedure is to improve balance between the breasts. However, perfect symmetry cannot be guaranteed.
After surgery, the breasts will appear perkier. Over the next 3–4 months, they will settle into a more natural shape and movement. While wearing a bra is recommended, it remains a personal preference.
Cup Size After Surgery: Why It’s Not Predictable
Despite many patients asking about post-surgical cup size, accurately predicting this measurement is not scientifically reliable due to variables such as:
- Differences in bra sizing between brands
- Post-surgical swelling
- Individual body proportions
Instead, the focus is on achieving a proportional, aesthetically pleasing result based on the patient’s goals and expectations.
Pain Management After Breast Reduction
Pain following breast reduction surgery is typically mild to moderate and well-managed with prescribed painkillers. Most patients experience discomfort for the first 48–72 hours after surgery, which gradually subsides.
Post-Surgery Bra and Clothing Advice
It is advisable to wait at least 3 months before investing in expensive bras or bikinis. This allows the swelling to subside and the breasts to settle into their final shape.
Recovery Timeline for Breast Reduction Surgery
- First 10–12 days: Dissolvable stitches are trimmed, and wounds are checked.
- First 3 weeks: Most patients can resume driving and return to work.
- 3–4 months: The final breast shape becomes more apparent as swelling resolves.
Understanding Surgical Incisions and Scarring
The incision pattern used in breast reduction surgery varies depending on the patient’s needs and surgical technique. The most common incision types include:
- Wise Pattern (Anchor Incision): Around the areola, vertically downward, and along the inframammary fold.
- Lollipop Incision: Around the areola and vertically downward, without the horizontal incision under the breast.
Scars will be most visible around the areola and upper vertical incision when standing or sitting without a bra. However, scars generally fade over time.
Benefits of Breast Reduction Surgery
Breast reduction surgery significantly enhances quality of life and has a high patient satisfaction rate. Some key benefits include:
✅ Relief from back, neck, and shoulder pain
✅ Improved posture
✅ Reduced skin irritation and chafing under the breasts
✅ Easier bra and clothing shopping
✅ Enhanced ability to exercise
✅ Boosted self-confidence and body proportion balance
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, breast reduction carries risks, though most complications are rare. The most common risks include:
Short-Term Risks
🔴 Bleeding (Hematoma): Occurs in a small percentage of patients and may require surgical drainage.
🦠 Infection: Affects 1–2% of patients and can be treated with antibiotics.
💢 Seroma (Fluid Collection): May require drainage.
Scarring and Wound Healing
📌 Hypertrophic/Keloid Scarring: Thick, raised, itchy scars occur in 3–5% of patients.
📌 Wound Dehiscence (Opening of the Incision): Uncommon but treatable with dressings.
Long-Term Risks
⚠️ Fat Necrosis: Occurs in 2–3% of patients, causing painful lumps that typically resolve over time.
⚠️ Changes in Sensation: Temporary nipple numbness is common; permanent loss occurs in some cases.
⚠️ Breastfeeding Challenges: 50% of patients may lose the ability to breastfeed post-surgery.
Rare but Serious Complications
🚨 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism: Rare but life-threatening.
🚨 Nipple Areola Complex (NAC) Loss: Occurs in 1–2% of cases, requiring prolonged healing and possibly further surgery.
🚨 “Dog Ears” (Excess Skin at the Sides): May require minor revision surgery after one year.
Pre-Surgery Preparations
Mammogram Screening
📌 Women 40+ years old should have a baseline mammogram before surgery.
Lifestyle Adjustments
🚭 Stop smoking 4 weeks before and 3 weeks after surgery to improve healing.
💊 Stop hormonal medications (HRT, birth control pills) at least 4 weeks before surgery to reduce blood clot risks.
🌿 Avoid herbal supplements 3–4 weeks prior to surgery as they may increase bleeding risks.
The Importance of Informed Consent
Understanding the risks, benefits, and limitations of breast reduction surgery is essential. Informed consent is not just a form to sign—it is an ongoing process from your first consultation to your final post-operative appointment.
Final Thoughts
Breast reduction surgery is a life-changing procedure with high success rates and significant physical and emotional benefits. While complications exist, they are generally rare. Clear communication with your plastic surgeon ensures realistic expectations and optimal results.
If you’re considering breast reduction surgery, schedule a consultation to discuss your individual goals, concerns, and suitability for the procedure.
References
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) – Breast Reduction Overview: www.plasticsurgery.org
- National Health Service (NHS, UK) – Breast Reduction Surgery Guide: www.nhs.uk
- Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery – “Long-Term Patient Satisfaction and Outcomes in Breast Reduction”: www.jprasurg.com
- Mayo Clinic – Risks and Recovery After Breast Reduction Surgery: www.mayoclinic.org